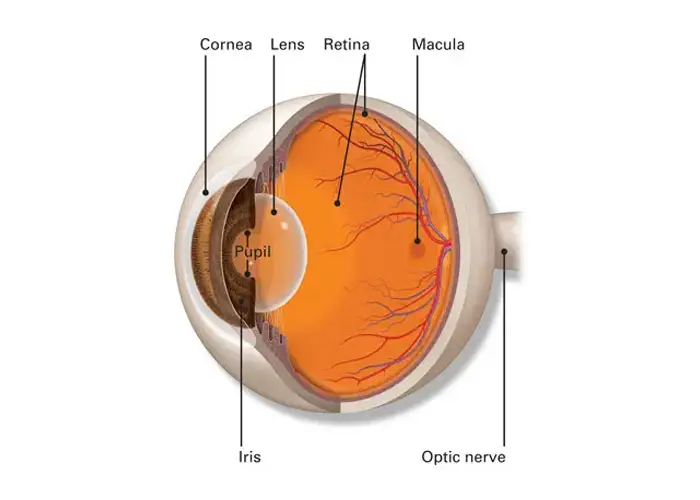
Retina and its Diseases
The Retina is the most sensitive part of the human eye that helps in converting light to useful information. It is fully packed with light-sensitive cells that act as a relay for communication which the brain processes as light and vision.
Retinal Detachment, Diabetic Retinopathy, Vein occlusions [CRVO and BRVO] and Age Related Macular Degeneration[ARMD] are some of the common diseases that affect vision. Treatment for retinal diseases both medical and surgical if initiated early on, can prevent permanent visual loss.
Symptoms
If you have retina disease, you may observe
Diabetic Retinopathy
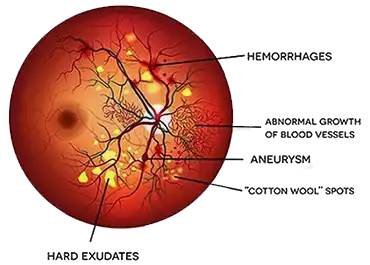
Diabetic Retinopathy is a disease observed in patients suffering from Diabetes Mellitus. Damage to the blood vessels due to high blood sugar is the main contributing causative factor for diabetes induced Retinal Damage. The tiny blood vessels in the Retina slowly start to deteriorate when you fail to maintain your sugar levels.
Diabetic patients are highly prone to develop diabetic retinopathy if they have prolonged uncontrolled blood sugar levels. The initial stages of the diseases are usually Asymptomatic and can be missed if not examined by an Eye Doctor.
As the disease progresses, it can cause significant permanent damage to the eyes including bleeding in the eye, swelling of the Retina and in its final stages, even Retinal Detachment for which patients will require Retinal Detachment Surgery.
Patient's symptoms vary significantly depending on the part of the layer involved. It can be as mild as seeing some minimal distortion in the vision to complete sudden loss of vision.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy
Control of Sugars
Strict control of your blood sugar levels by appropriate medication, diet, exercise along with regular follow ups with your diabetologist is the first step in protecting your eyes from Diabetic Retinopathy.

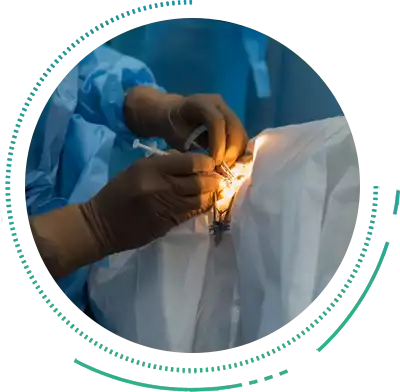
Intravitreal Injection
Anti-VEGF Molecules
The use of Anti-VEGF drugs in Diabetic Retinopathy Eye Treatment has shown excellent results over the years. Anti-VEGF molecules have a dual effect of reducing abnormal blood vessels as well as reducing Retinal Swelling[Macular Edema]. Anti-VEGF injections have to be regularly administered to keep the profile stable since their duration of action usually lasts for 4-5 weeks. These are the most recommended treatments in diabetes induced disease.
Steroid Preparations
Steroid Preparations can be administered into the Vitreous Cavity either as is or via a long lasting implant which releases the drug slowly. Steroid injections can be tried in cases where adequate improvement with Anti-VEGF compounds is not observed or in cases where regular injections may not be possible in the Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment. However, steroid injections can increase the pressure within the eyes and may cause Glaucoma.
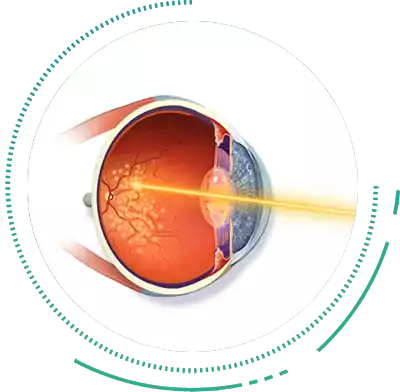
Retinal LASER Photocoagulation
Laser Photocoagulation is a Retinopathy Treatment which is reserved only for the stage of Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment, i.e Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Laser Treatment works by shrinking the abnormal, leaky and fragile blood vessels, which if left unchecked can lead to Bleeding and Retinal Detachment.
Laser Photocoagulation is a sight saving procedure and is a must for these advanced cases. Laser may be combined with other Eye Treatments, such as during Retinal Detachment Surgery, to treat complications due to Diabetic Retinopathy. LASER may also be used after Retinal Detachment Treatment to seal the Retina in place.
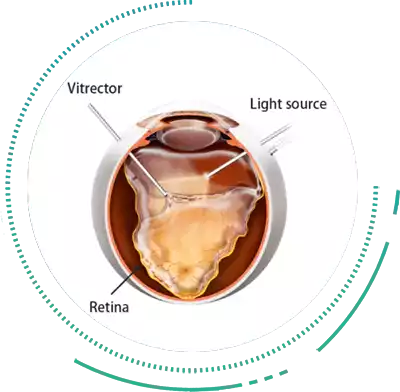
Pars Plana Vitrectomy
Pars Plana Vitrectomy Eye Treatment is an effective Retina Surgery, to treat Diabetic Retinopathy, Retinal Holes, Retinal Detachment Treatment and bleeding. Vitrectomy Surgeries are usually reserved for end stage or complicated Diabetic Retinopathy when all medical management fails or when Retinal Detachment Treatment is required.
Vitrectomy Surgery involves the removal of the Vitreous, i.e the jelly like substance in the back of the eye, followed by further interventions such as Retinal Detachment Treatment, lasering the Damaged Retina or Peeling Abnormal Membraned from the Retinal Surface. After this Vitrectomy Retina Surgery, a tamponading material is left inside the eye, usually silicone oil, in diabetics, which is removed at a later date usually 4-6 months after the first Retina Surgery.
It is important to note that during the presence of the tamponading material in the Vitreous Cavity, the patient's vision will be blurred. Temporary glasses may be given at this time to enable you to carry out essential activities within a few weeks after the Retina Surgery.
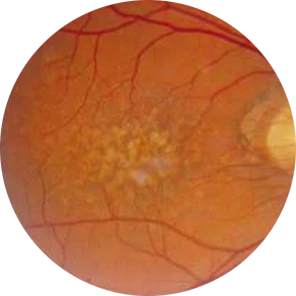
Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Age-Related Macular Degeneration is a major disease of the retina which affects the elderly. The condition results from abnormal deposition of metabolic waste products on the base of the pigment epithelium layer complex and its consequences. This weakens the retinal watertight barrier and causes abnormal blood leaky blood vessels to encroach into the central-most extremely sensitive area known as Macula.
This causes the Macula to swell and distort, causing the central fine vision to be affected. If left unchecked, these abnormal vessels cause scarring which leads to Permanent Visual Loss. In the early stages, ARMD may not have any symptoms. As the condition worsens, patients initially complain of distortion of central vision, e.g. straight lines looking crooked, or objects appearing smaller or larger than they actually are.
Advanced ARMD usually causes complete loss of the central vision while sparing only the peripheral vision. Regular Eye Examination can help in the early diagnosis and prevention of Visual Loss due to ARMD. These days, treatments are available with good outcomes to treat visual loss caused by Age-Related Macular Degeneration.
Treatment Options
Observation and Lifestyle Modifications
Since ARMD is a disease primarily caused by deposition of metabolic waste products and its toxic effects, reducing the effects of oxidant compounds plays a key role in reducing the severity of the disease. Patients are strictly advised to stop smoking permanently as this is a key risk factor for accelerating ARMD.
Oral supplements of antioxidants like lutein, zeaxanthin, vitamin C, etc are helpful in slowing down the course of the disease. Another important risk factor is the use of bright screens for prolonged periods of time. This can accelerate the progression of this disease at an earlier age.

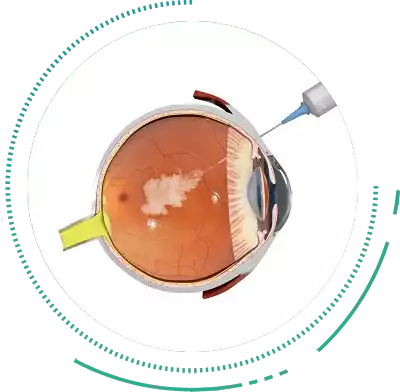
Intravitreal Injections
Intravitreal Injections of Anti-VEGF molecules are the treatment of choice for the wet form of Macular Degeneration. The medicine is injected into the vitreous cavity to stop the growth of and shrink the abnormal blood vessels that cause distortion of the Macula. As is the case with Diabetic Retinopathy, repeated Intravitreal Injections at regular intervals are usually required to keep the vision stable.
Low Vision Aids
When ARMD is extremely advanced with associated scarring of the macula area, vision cannot be restored. The only options left at this stage is to use low vision aids that stimulate the surrounding healthy macula to see moderately well enough to allow essential day to day activities. Retina Surgery for ARMD is usually not indicated.

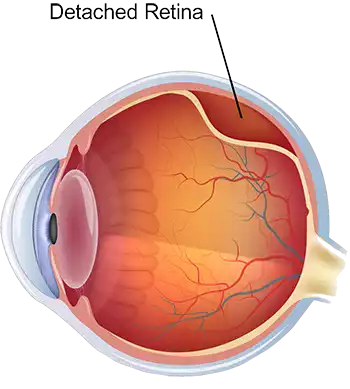
Retinal Detachment
Retinal Detachment is a serious eye condition, wherein the light sensitive retina starts detaching from the choroid. This condition requires immediate attention either in the form of Retinal Detachment Treatment or Retinal Detachment Surgery to prevent permanent Vision Loss. Retinal Detachments have numerous causes including retina tears and holes and pathologies such as Diabetic Retinopathy, inflammations in the choroid, among others.
Rhegmatogenous Detachment Rhegmatogenous Detachment is most commonly observed as a consequence of a Retinal hole or a tear. These holes or tears can occur in the borders of the retina and can go unnoticed if not examined under dilatation of the pupils. They are more commonly seen in people with Myopia [Short-Sight] and hence it is recommended that people with myopia should undergo a compulsory complete dilated fundus testing atleast once a year. In our experience we have also seen these holes occurring in patients without any refractive error in the eye.
As the Retina holes enlarge, the overlying liquified vitreous seeps into these holes and creates a separation between the retina and the choroid causing a Retinal Detachment. Rhegmatogenous RD’s progress faster and can involve the central vision within a span of hours or days and would need Retinal Detachment Surgery at the earliest.
Treatment Options
Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachments lead to a sudden onset of vision loss and needs Retinal Detachment Surgery at the earliest, without which the prognosis or visual recovery rapidly deteriorates. Retinal Detachment Treatment has evolved significantly over the last two decades with considerable safety and efficacy.
Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy Surgery is the most preferred and practiced Retinal Detachment Treatment. The gold standard to treat these Rhegmatogenous Detachments is usually via Pars Planar Vitrectomy with fluid gas exchange and endolaser.
A tamponading agent, either perfluorooctane gas or silicon oil is usually used to keep the retina in place after the Retina Surgery until it re-attaches. Vitrectomy Surgery restores vision loss by treating the detachment. Retinal Detachment Vitrectomy is safe to undergo and gives maximum patient satisfaction and good results if performed early on.

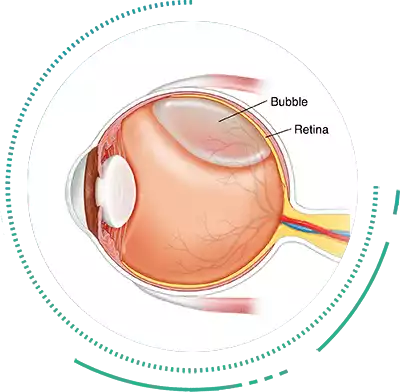
Pneumatic Retinopexy With Scleral Buckling
Pneumatic Retinopexy with Scleral Buckling method is a less invasive Retina Surgery for treating Rhegmatogenous RD’s. Although not commonly performed now, it is still used in a few cases. The Retina Surgeon injects a gas bubble that tends to expand within the eye thus re-positioning back the Retina Detachment.
Pneumatic Retinopexy is suitable for treating small tears or Detachments. Based on your retinal condition and the severity of the detachment, the Retinal Surgeon will decide on a combination of Retinal Detachment Treatment methods. Retinal Detachment Surgery usually take about 90 minutes and patients are advised to take 3 to 4 weeks rest for complete recovery after the Retina Surgery.
Tractional Retinal Detachment
Tractional Retinal Detachment is a type of Retinal Detachment caused by abnormal growth of blood vessels in the eye. These blood vessels are sticky and attach to the retina frequently. The blood vessels also secrete a fibrous component which contracts and pulls the retina causing it to detach. Abnormal growth of blood vessels also known as Neovascularization are seen in patients having
- Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy
- Vein Occlusions
- Ocular Ischaemic Syndrome
- Eale's disease
- Retinopathy of Prematurity
- Ocular Inflammation with Vasculitis
Treatment Options
The first step in tractional Retinal Detachment Treatment is to identify the cause of the disease and control it [e.g control of diabetes,etc]. The next step is to reduce the amount of abnormal blood vessels in the eye by performing Pan-Retinal Laser Photocoagulation where possible in the Detachment Treatment. The latest in this procedure is the use of Multispot Laser Therapy which reduces laser time to 1/10th of conventional laser methods.
Vitrectomy
If the Tractional Detachment is already involving the centre-most sensitive area i.e the Macula, then Retinal Detachment Surgery is usually performed at the earliest treatment. The standard of care these days is Sutureless Vitrectomy, wherein the abnormal attachments of the blood vessels to the retina are released very carefully during the Detachment Surgery.
This Retinal Detachment Surgery is a time-taking process, where the Retina Surgeon has to manually peel all the attachments away so that the retina is released from these abnormal blood vessels. Once the retina is free, an additional laser is performed with the help of a specialized probe [Endolaser] which prevents the re-growth of these abnormal blood vessels. A tamponading agent i.e silicon oil is usually placed inside the eye to keep the retina well opposed. The silicon oil is usually removed 6-9 months later as a separate Retina Surgery Procedure.
Exudative Retinal Detachment
Exudative Retinal Detachment is caused by any inflammatory condition of the eyes such as infections, autoimmune conditions, etc. The severe inflammation causes the retina to separate from the choroid causing a Retinal Detachment. Patients usually present with a sub-acute loss of vision which can affect both the eyes. There may also be some history of pain and redness in the eyes for a few days prior to the loss of vision.
Treatment Options
Exudative Retinal Detachment Treatment does not need any Retinal Detachment Surgery. Once the primary cause of the inflammation has been identified and treated without delay, Exudative Retinal Detachments settle automatically with good visual recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens after Vitreoretinal Surgery?
It is very common that you may experience a swollen eye, or red or eye tenderness for a couple of weeks. Also, you may have a blurry vision accompanied with a mild pain. Normal stage will be restored within 3 to 4 weeks of time after Detachment Surgery. You may also need to maintain a face-down position for a prescribed length of time if necessary during the Retina Treatment.
Is Retinal Laser Surgery Painful?
Conventional Retinal LASER Treatment causes mild discomfort to the eye. However at Sri Eye Care we use a pattern scan multispot LASER which uses a shorter LASER exposure time and delivers multiple spots in one shot onto the Retina. This reduces the Retina Detachment discomfort, as well as reduces Retina Eye Treatment time to 1/10 th of conventional LASERs.
How does Diabetic Retinopathy affect vision?
The abnormal blood vessels associated with Diabetic Retinopathy boosts the growth of scar tissue that eventually pulls the retina away from the eye. This results in the floating vision, and eventually to being blind. The diabetes also affects the central vision by causing swelling of the Central Retina [Macula]. This is called as Diabetic Maculopathy/Macular Edema.
How long will I be dilated?
Once you have received the dilating drops, it may take around 30 minutes for your pupils to fully open. Pupils of diabetic patients take a longer time to dilate, so it may take upto 45minutes. The effect of dilatation may last up to six hours, usually.
How long will my appointment take?
Although routine appointments at Sri Eye Care take around 25-30 mins, appointments made for a retina check-up can take upwards of 60-90 minutes. This may increase in case additional diagnostic scans are advised. If there a LASER advised, each LASER sitting should take around 15-20 minutes after dilatation.
Why would I need to take repeat injections?
Only a small amount of Anti-VEGF [0.1ml] can be injected into the eye at one time. At this dosage, the effect of the drug lasts only for a period of 4-5 weeks. As the disease process is still active in the eye, you would need repeated injections until the leaking vessels regress.






